Agassiz Life Sciences: Case Study
From the information provided in the case study, it is evident that Agassiz Life Sciences is facing a difficult situation regarding developing and launching its innovative biomedical device in the market. From a strategic point of view, it is critical to underscore that the firm founders did not focus on formulating their vision and mission, yet they are the essential management tools for attaining both short-term and long-term business goals. In addition to the lack of vision and mission statements, the two entrepreneurs had not confirmed that the new technological application would work. In fact, it failed when being tested in a research facility, a fact that made many investors in the venture get worried that would not recoup their funds. This memo aims to:
- Identify all relevant stakeholders and their interests
- Highlight strategic intent, governance, and associated ethics regarding critical considerations
- Detail evaluation scenarios for the main stakeholders in the venture
- Provide recommendations to the Board of Agassiz that would go a long way in helping them to proceed
Stakeholders and their interests
- The first group of stakeholders in the venture are the founders of the business, Alex and Woody. Although they initially agreed to own the company on a 50-50 basis, circumstances have forced them to change the agreement. Currently, Alex is interested in retaining her job as the CEO, which would enable her to retain a constant salary help the company grow. On the other hand, Woody, an engineer by profession, is focused on developing the innovative product that would help persons across the world attain better care outcomes.
- Doyle is another stakeholder interested in investing and making good returns. His interest is to own a 52% of the firm by injecting $6.5 million. This would result in a majority share in the investment.
- In 2013, Angel investors injected $1.2 million into the company with a promise to get a 50% share, but things have so far changed. They are disappointed since it is taking too long to realize returns.
- Series B investors contributed a total of $3.3 million in 2014, which represented 44% of the firm’s equity. These investors are patient until the firm things rolling.
- Finally, BD Biosciences, a leading supplier of biomedical instruments, is interested in acquiring the core technology at $7.0, but Woody must be willing to perfect it.
Strategic intent, governance, and associated ethics regarding critical considerations
- A strategic intent is composed of competitive moves and unique approaches that are applied by business managers. It helps to define management’s action plan that is crucial to attracting and pleasing customers, growing business, and conducting operations (Rothaermel, 2012). Regarding the firm in the case study, it is apparent that the founders did not adopt a strategic intent, which is the reason why the firm is almost crumbling.
- The following five processes are applied in adopting a business strategy: goal setting, analysis, strategy formulation, strategy implementation, and evaluation and control (Rothaermel, 2012).
- Business entities are guided by clear structures of governance that should be as shown in the figure below.
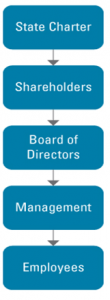
Figure 1. A diagram showing the flow of authority in many firms that adopt effective corporate governance.
- In addition, CSR approaches have been shown to go hand in hand with a competitive advantage in many companies (Rothaermel, 2012).
- This pyramid is widely used to show various aspects of CSR
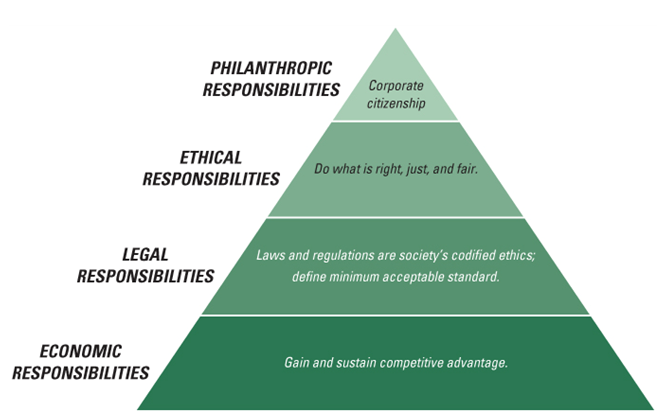
Figure 2: A pyramid showing different responsibilities in the CSR model.
- However, approaches should be tailored to reflect ethics of doing business (Rothaermel, 2012). For instance, it would be unethical to adopt some strategic aspects with the goal of making some stakeholders gain less in a venture.
- A strategic leader who adopts effective governance would play roles as shown in the diagram below.
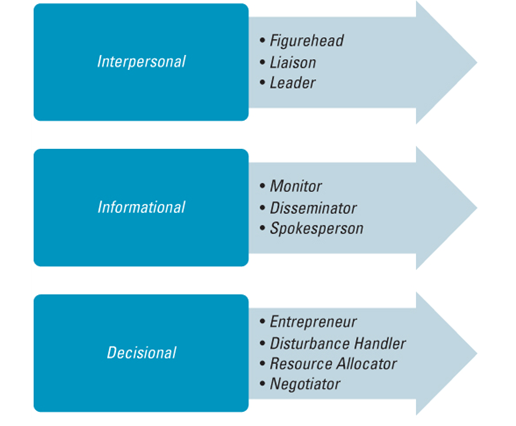
Figure 3: Roles played by a strategic leader.
Equity ownership
Prior periods
| 2012 %Equity | 2012 $Value | January 2013 %Equity | January 2013 $Value | January 2014 %Equity | January 2014 $Value | |
| Founders | 100 | 1.2 million | 50 | 1.2 million | 28 | 2.1 |
| Series A | – | – | 50 | 1.2 million | 16 | 1.2 |
| Employees | – | – | – | – | 12 | 0.9 million |
| Series B | – | – | – | – | 44 | 3.3 million |
| Total | 100% | 1.2 million | 100% | 2.4 | 100% | 7.5 million |
January 2015: Equity shares and values; three scenarios
| Agassiz’s plan %Equity | Agassiz’s plan $Value | DFC’s revised offer %Equity | DFC’s revised offer $Value | BDB’s buyout offer %Equity | BDB’s buyout offer $Value | |
| Founders | 16 | 2.4 million | 2.4 | 0.3 | 28 | 1.96 |
| Series A | 8 | 1.2 million | 9.6 | 1.2 | 16 | 1.12 |
| Employees | 6 | 0.9 million | 7.2 | 0.9 | 12 | 0.84 |
| Series B | 22 | 3.3 million | 26.4 | 3.3 | 44 | 3.08 |
| Series C | 48 | 7.2 million | 52 | 6.8 million | – | – |
| Total | 100% | 15 million | 100% | 12.5 million | 100% | 7 million |
Recommendations
For the firm to proceed, the four board members should:
- Adopt a strategic plan that should have clear vision and mission statements
- Seek other ways of obtaining funds, such as bank loans.
- Focus on developing a functional biomedical testing machine that would help the firm gain a competitive advantage.
- Work on a better share holding structure that can only be altered with the approval from all shareholders.